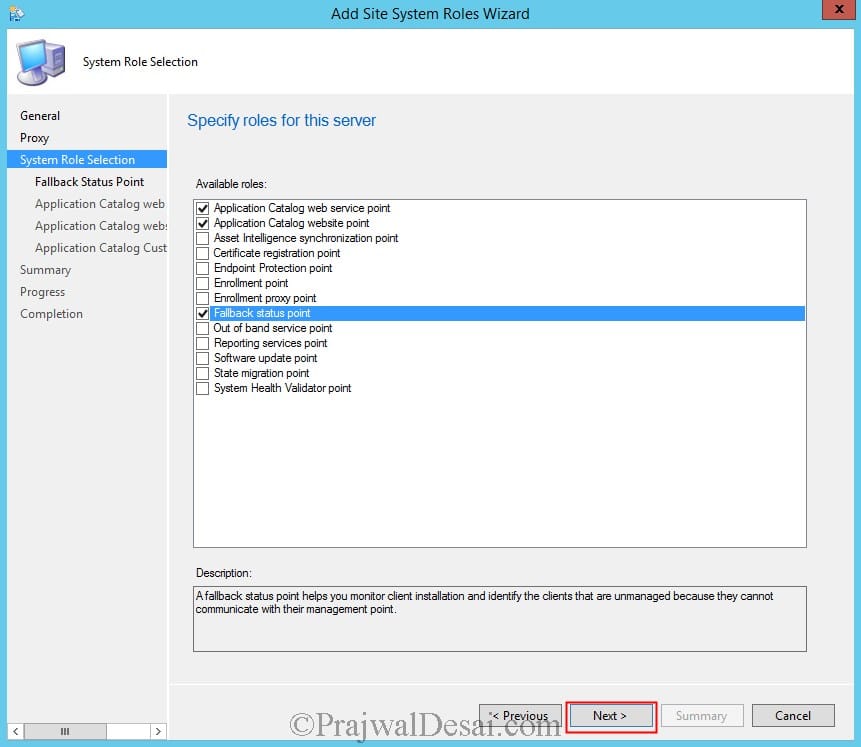
Install System Health Validator Point Sccm 2012 R2
A quick table summarising all of the prerequisites for site system roles for ConfigMgr 2012. Configuration Manager uses site system roles to support management operations at each site. When you install a Configuration Manager site, some site system.
SCCM Log files . D: \Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager\Logs)Management Point Logs: < Program files of install drive> \SMS. D: \Program Files\SMS. Benvista Photo Zoom Pro 5 0 2016. There are bucketloads of logs to check in SCCM – and knowing which one is the right one simply takes time and experience. However, that’s where google – and possible the list below of all log files, will be able to help you. List of log files. A complete list of log files can be found at https: //technet. However, for ease, I have dumped them into a single table – available below.
- Download the free trial version below to get started. Double-click the downloaded file to install the software.
- SCCM uses a lot of log files, it could be quite confusing finding what you need. I gathered a list of all the log files and a description of their content to.
Maintains the local package cache on the client. Client. Ccm. 32. Bit. Launcher. log. Client operations. Records actions for starting applications on the client marked as . This log file also includes information about enabling and disabling wake- up proxy. Client. Ccm. Messaging.
Client operations. Records activities related to communications between the client and management points. Client. CCMNotification. Agent. log. Client operations. Records activities related to client notification operations. Client. Ccmperf. log.
Client operations. Records activities related to the maintenance and capture of data related to client performance counters.
Client. Ccm. Restart. Client operations. Records client service restart activity. Client. CCMSDKProvider. Client operations. Records activities for the client SDK interfaces. Client. Certificate.
Maintenance. log. Client operations. Maintains certificates for Active Directory Domain Services and management points. Client. CIDownloader.
Client operations. Records details about configuration item definition downloads. Client. CITask. Mgr. Client operations. Records tasks that are initiated for each application and deployment type, such as content download or install or uninstall actions. Client. Client. Auth. Client operations.
Records the signing and authentication activity for the client. Client. Client. IDManager. Startup. log. Client operations. Creates and maintains the client GUID and identifies tasks performed during client registration and assignment. Client. Client. Location. Client operations.
Records tasks that are related to client site assignment. Client. CMHttps. Readiness. Client operations. Records the results of running the Configuration Manager HTTPS Readiness Assessment Tool. This tool checks whether computers have a PKI client authentication certificate that can be used for Configuration Manager. Client. Cm. Rc. Service. Client operations.
Records information for the remote control service. Client. Content. Transfer. Manager. log. Client operations.
Schedules the Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) or the Server Message Block (SMB) to download or to access packages. Client. Data. Transfer. Service. log. Client operations. Records all BITS communication for policy or package access. Client. Endpoint. Protection. Agent.
Client operations. Records information about the installation of the Endpoint Protection client and the application of antimalware policy to that client.
Clientexecmgr. log. Client operations. Records details about packages and task sequences that run on the client. Client. Expression. Solver. log. Client operations. Records details about enhanced detection methods that are used when verbose or debug logging is enabled.
Client. External. Event. Agent. log. Client operations. Records the history of Endpoint Protection malware detection and events related to client status. Client. File. BITS. Client operations.
Records all SMB package access tasks. Client. File. System. File. log. Client operations. Records the activity of the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) provider for software inventory and file collection. Client. FSPState.
Message. log. Client operations. Records the activity for state messages that are sent to the fallback status point by the client. Client. Internet. Proxy. log. Client operations. Records the network proxy configuration and usage activity for the client.
Client. Inventory. Agent. log. Client operations. Records activities of hardware inventory, software inventory, and heartbeat discovery actions on the client.
Client. Location. Cache. log. Client operations. Records the activity for location cache usage and maintenance for the client. Client. Location. Services. log. Client operations. Records the client activity for locating management points, software update points, and distribution points. Client. Maintenance.
Coordinator. log. Client operations. Records the activity for general maintenance task activity for the client. Client. Mifprovider. Client operations. Records the activity of the WMI provider for . MIF files. Clientmtrmgr.
Client operations. Monitors all software metering processes. Client. Policy. Agent. Client operations. Records requests for policies made by using the Data Transfer service. Client. Policy. Agent. Provider. log. Client operations.
Records policy changes. Client. Policy. Evaluator. Client operations. Records details about the evaluation of policies on client computers, including policies from software updates.
Client. Policy. Platform. Client. log. Client operations. Records the process of remediation and compliance for all providers located in %Program Files%\Microsoft Policy Platform, except the file provider. Client. Policy. Sdk. Client operations.
Records activities for policy system SDK interfaces. Client. Pwrmgmt. log. Client operations. Records information about enabling or disabling and configuring the wake- up proxy client settings. Client. Pwr. Provider. Client operations.
Records the activities of the power management provider (PWRInv. Provider) hosted in the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) service. On all supported versions of Windows, the provider enumerates the current settings on computers during hardware inventory and applies power plan settings. Client. SCClient.
This data is logged in Mtrmgr. Client. User. Affinity. Client operations. Records details about user device affinity. Client. Virtual. App. Client operations.
Records information specific to the evaluation of App- V deployment types. Client. Wedmtrace. Client operations. Records operations related to write filters on Windows Embedded clients. Clientwakeprxy- install. Client operations.
Records installation information when clients receive the client setting option to enable wake- up proxy. Clientwakeprxy- uninstall. Client operations.
Records information about uninstalling wake- up proxy when clients receive the client setting option to disable wake- up proxy, if wake- up proxy was previously enabled. Clientccmsetup. log.
Client installation. Records ccmsetup tasks for client setup, client upgrade, and client removal. Can be used to troubleshoot client installation problems.
Clientccmsetup- ccmeval. Client installation. Records ccmsetup tasks for client status and remediation.
Client. Ccm. Repair. Client installation. Records the repair activities of the client agent.
Clientclient. msi. Client installation. Records setup tasks performed by client.
Can be used to troubleshoot client installation or removal problems. Clientscxcm. log. Client for Linux and UNIXThis is the log file for the core service of the Configuration Manager client for Linux and UNIX (ccmexec.
This log file contains information about the installation and ongoing operations of ccmexec. Clientscxcmprovider.
Client for Linux and UNIXThis is the log file for the CIM service of the Configuration Manager client for Linux and UNIX (omiserver. This log file contains information about the ongoing operations of nwserver. Client. CCMClient- .
Client for Mac Computers. Records activities that are related to the Mac client operations, which includes application management, inventory, and error logging. Client. CCMAgent- .
Client for Mac Computers. Records information that is related to client operations, which includes user logon and logoff operations and Mac computer activity.
Client. CCMNotifications- . Client for Mac Computers. Records activities that are related to Configuration Manager notifications displayed on the Mac computer. Client. CCMPref. Pane- .
Supported Configurations for Configuration Manager. The maximum number of clients (devices) that a site can support depends on the site type, and the version of Configuration Manager that you use.
Although you can only assign a device to a primary site, secondary sites support communications from devices. To help identify the supported number of devices, devices are divided into three logical client groups. A site is not limited to supporting devices from a single client group. A primary site can support a separate number of devices from each of the three client groups. For example, a stand- alone primary site that runs Configuration Manager SP1 can support up to 1. However, Configuration Manager does not support replacing any number of devices from one client group with devices from another client group. For example, you have a stand- alone primary site that has 1.
In this scenario, the site cannot support additional devices from client group 1 even though it is not supporting additional clients from the additional client groups. The following table identifies the maximum number of devices per client group that are supported at primary and secondary sites: Tip The maximum number of clients that a primary or secondary site can support is not affected by the edition of SQL Server you use at that site. However, a child primary site that uses a local site database (installed on the site server) is limited to 5. Site type. Configuration Manager version.
Client group 1. Client group 2. Client group 3. Stand- alone primary site, with a local site database, or a remote site database. System Center 2. 01.
Configuration Manager with no service pack 1. System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager with SP1. System Center 2. 01. R2 Configuration Manager. System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager SP2.
System Center 2. 01. R2 Configuration Manager SP1. Child primary site with a local site database.
System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager with no service pack 1.
System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager with SP1. System Center 2. 01.
R2 Configuration Manager. System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager SP2.
System Center 2. 01. R2 Configuration Manager SP1. Child primary site with a remote site database. System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager with no service pack 1.
System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager with SP1. System Center 2. 01. R2 Configuration Manager.
System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager SP2. System Center 2. 01. R2 Configuration Manager SP1. Secondary site. Any version. Beginning with System Center 2. Configuration Manager SP2)1.
System Center 2. 01. Configuration Manager with no service pack does not support the client for Linux and UNIX (client group 1) and does not support the client for Mac (client group 3). Additionally, client group 2 includes only mobile devices supported by using the Exchange Server connector. Support for the additional device types in this client group is available beginning with System Center 2. Configuration Manager SP1. Beginning with System Center 2.
Configuration Manager SP1, primary sites support Windows Embedded devices that have File- Based Write Filters (FBWF) enabled. When embedded devices do not have write filters enabled, a primary site can support a number of embedded devices up to the allowed number of devices for that site (5. Of the total number of devices that a primary site supports, a maximum of 1.
Windows Embedded devices when those devices are configured for the exceptions listed in the Deploying the Configuration Manager Client to Windows Embedded Devices section in the Introduction to Client Deployment in Configuration Manager topic. A primary site supports only 3,0. Windows Embedded devices that have EWF enabled and that are not configured for the exceptions. In a hierarchy that has a central administration site that uses a Standard edition of SQL Server, child primary sites are limited to 5. When a site supports only devices from client group 2, the site can support up to 1. With this configuration, there is no change to the total number of devices that are supported in the hierarchy. Each secondary site can support communications from up to 5,0.
This number includes a mix of devices from any of the three client groups. A secondary site could support communications from additional devices when its hardware configuration exceeds the recommended hardware configuration. Beginning with System Center 2. Configuration Manager SP2, sites that meet the updated recommended hardware requirements, and that have a fast and reliable network connection to other sites and site system servers, can support the updated number of devices.
For information about the recommended hardware for Configuration Manager sites, see Planning for Hardware Configurations for Configuration Manager.